STRUCTURE OF CFGS
The CFGS system has a simple structure consisting of many parts, each with its own function and role described in the diagram below:
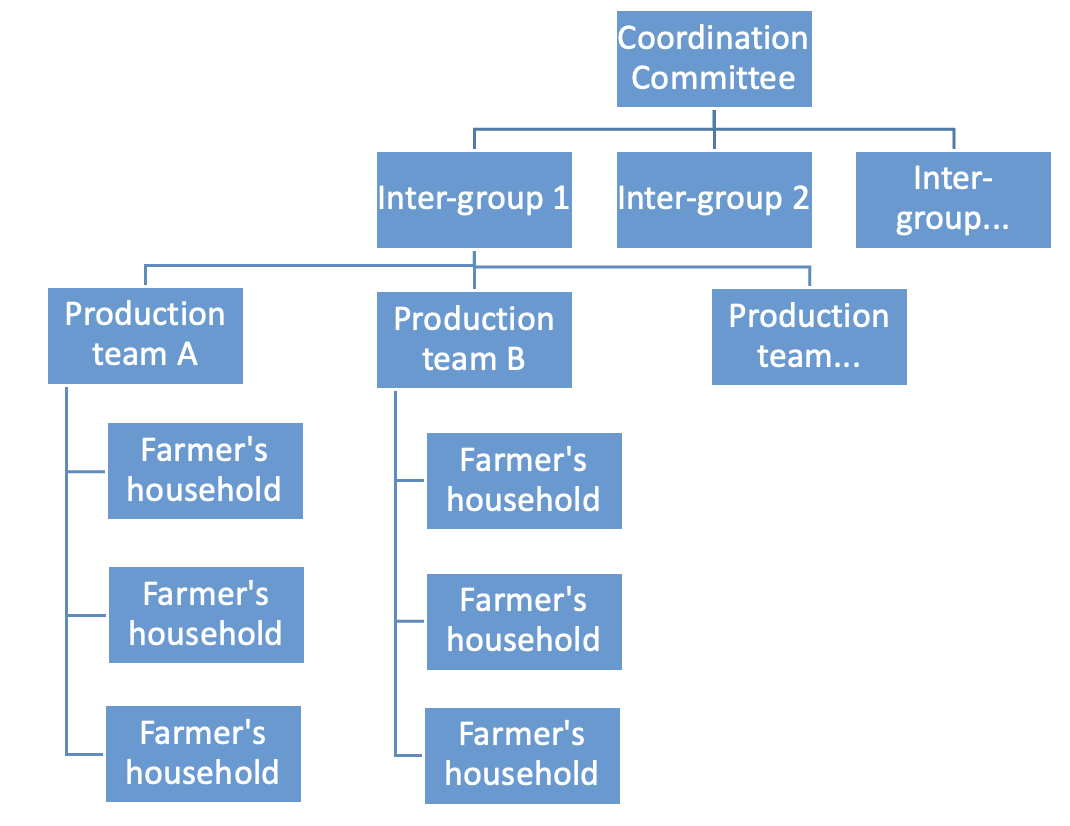
1.1. Farmer's household
To participate in the Production group, farmers must contact the producer group leader in their area.
Function and mission:
- Farmers belong to a production group
- Learn the principles and methods of organic production.
- Learn and understand about organic standards
- Actively participate in activities proposed by the Production team and CFGS: group meeting, training, inspection, etc.
- Complete the farm management plan and update it every year
- Complete the commitment of organic farmers and follow the commitment.
- Provide organic products and ensure their quality.
- Encourage and help other farmers to participate in CFGS.
- Environmental protection, ecological diversity
- Publicity and transparency in the production process
- Share and spread the experience
- Learn, exchange and promote products
- Complete production log
1.2. Production Team
How to form (set up) a production group
- Any farmer can start a “production group” of organic farmers. The Production Group should have at least 3 farming households living close to each other (specifically, the members know each other and know each other's production areas).
- Production team members have similar production systems
- To form a group, the production team must complete the production group's CFGS membership registration form and send it to the CFGS coordination committee.
- The Coordination Committee allocates the production group into the appropriate intergroup. The inter-team will contact and work directly with the production team. The process begins with training farmers in the CFGS organic standard production group and completing their pledge application.
- The production team will ensure that all members who are organic producers complete the commitment form, read and learn the summary of the basic CFGS standards that have been provided.
Functions and duties:
- The production group builds its own rules and regulations with the participation and consensus of all members. The rules and regulations must be documented and sent to the coordination board a copy to ensure that these rules and regulations do not conflict with the general regulations of CFGS.
- Must have a specific group structure and assignment of tasks
- Organize regular meetings and save meeting minutes as well as related records.
- Between group members, there must be support activities, sharing experiences, helping each other (production, sales, book management ...)
- Complete the CFGS documents and submit to the intergroup. Ensure members understand the CFGS standard
- Participate in cross-inspection when required by inter-groups
- Motivate team members to achieve group goals and objectives.
- Ensure fairness and avoid conflicts of interests of members.
- Group planning
- Team coordination: organizing production, packaging - distributing products, coordinating labor
1.3. Intergroup
How to form an intergroup
- Responsibility for the establishment of the inter-group rests with the coordination group. When receiving requests from farmers or production groups. The process of forming an intergroup will begin.
- An intergroup includes a number of production groups in a given area. Members include representatives of all production groups as well as representatives of relevant members from outside such as consumers, customers, technicians, local authorities, farmer trainers, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), non-profit organizations (NPOs) or interested individuals/organizations.
- In the intergroup, non-farmer members can contribute to the preparation of reports, preservation of data and participation in monitoring or decision-making processes. They will commit to being members of the Intergroup for about 2 years.
- The inter-group will select a management board from among the inter-group members to be responsible for the overall activities of the inter-group.
- During the activity, the inter-group will choose:
- Certification Board (number of members depends on the intergroup but should include both farmer and non-farmer members): review the inspection reports of the producer groups to decide determine the certification status for farmers, urge, monitor and issue disciplinary action for violations.
- Certification director (certification manager): details are included in the appendix
Functions and duties:
- Regular meeting
- There must be structure and division of responsibilities
- Connecting organic farmers with CFGS and partners
- Coordinating the process of periodic and random cross-inspection
- Support training, training on organic agriculture and CFGS standards
- Store data, CFGS records and related papers of Production teams
- Make a decision to certify and suspend certification for the Production group when there are violations
- Decide on inspection fees for certification
- Complete and send the annual report to the Coordination Board
- Accompany farmers to find solutions for the field and support market connection for the production group's products.
- Working exchange and consulting for the coordination board
- Support working connection between production team and customers
1.4. Coordination committees
How to set up a coordination committee?
- The CFGS Coordination Committee consists of five different members of the CFGS system who volunteered to participate.
Members are selected at the annual meetings of the CFGS.
- The term of the members (officers) of the coordination committee is 2 years
- The Coordinating Board selects an administrator who will be responsible for maintaining the CFGS system databases, issuing certificates and communicating between the CFGS and the coordination committee.
- The Coordinating Board appoints a standards committee to review organic standards as well as input materials. Changes to the organic standard are presented at the annual meeting of the CFGS for ratification. The members of the standards committee can be outsiders or even outside CFGS member organizations (for example an expert from the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development or a university professor. )
Functions and duties:
The CFGS Coordinating Committee is responsible for the major issues common to intergroups in general
- The Coordinating Board is responsible for managing the entire CFGS system, especially regarding the integrity and standards of the CFGS system.
- Protect the interests of intergroup, farmers and CFGS
- Maintain and update CFGS organic standards and approve production input guidelines
- Receive applications from new production groups and distribute them to the appropriate intergroup
- Support production teams and intergroup to improve procedures and systems
- Receive information/reports from inter-groups
- Issue certification or refuse to issue certification if the inter-group does not do it correctly
- Promote organic products
- Responsible for managing CFGS's own sign (trade name). Therefore, the coordination committee has the right to inspect the internal activities of production groups and intergroup when required.
- Connect with domestic and international organic farmer’s network
- Support training for production groups on organic agriculture, CFGS standards and necessary skills.
- Inspect, supervise, support intergroup, production groups and farmers.
- Handling inter-group violations
- Report to higher levels and local team
- Promote and contact local news agencies
- Market link
- Maintain CFGS data system including:
• Basic information of production groups
• Detailed information on each producer's certification status
Copies of certification decisions for farmers from intergroup Documenting violations and the correction process.
File
20 structure.pdf
(73.78 KB)
|
